2.4 Industry 4.0 and The Factory of the Future
Industry 4.0 represents the fourth major transition in the history of the industry. The term was originally coined by the German Federal Government as part of its high-tech strategy. Industry 4.0 means the intelligent networking of machines and processes in the industry with the help of information and communication technology.
The Internet is the core technology for the changes within the framework of Industry 4.0.
Goals of Industry 4.0 are:
- – productivity increases
- – cost reductions
- – flexibilisation of production
The integration of IT into the production process means massive changes in the work tasks. This has consequences above all for the qualification profiles of the skilled workers in the companies, the engineers with practical experience and above all the trainees. In order for workers to take advantage of the new opportunities, new ideas for work design and competence development need to be developed. These changes also affect vocational schools and the way of learning there.
At the vocational school in Wolfsburg, teachers have been dealing with this issue for several years. They have developed a new innovative approach to how the latest Industry 4.0 technologies can be taught and learned in school: a smart filling plant.
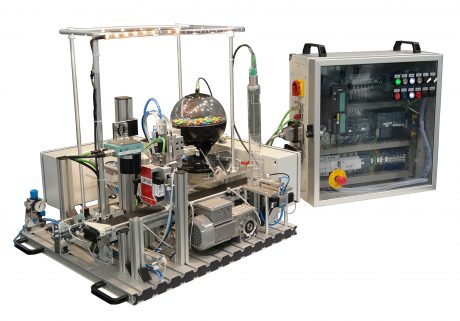
In the following video, we are asking the teacher about how they integrated Industry 4.0 into the teaching practice.
Reflection
Interoperability and autonomy are two important keywords in this context. The internet is to be used to establish a system-based connection between all people and objects involved in the production process such as machines, transport containers, and transport equipment. In addition, all machines and manufactured products will be equipped with communication technologies. This allows machines to communicate continuously and in real-time. The objects not only exchange information with each other but also transmit their data to various IT systems.
In so-called Smart Factories programmed algorithms independently control machines and react intelligently to current framework conditions. A prominent example of the smart factory of the future is Factory 56, which is currently being built by the Mercedes-Benz plant in Sindelfingen (Germany). Factory 56 is being planned as a digital, flexible smart factory on 220.000m2. Production planning, control, and quality assurance will rely on artificial intelligence, big data analyses, and predictive maintenance.
Activity
Would such a project also be interesting for your school/institution? Make a comment 💬👇.
Deepening
Get more information about the school project. 👉 click here.
One thought on “2.4 Industry 4.0 and The Factory of the Future”
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.

This project is interesting for me. As a TVET teacher educator, I can get my teachers involved.